朴素贝叶斯应用:垃圾邮件分类
1. 数据准备:收集数据与读取
2. 数据预处理:处理数据
3. 训练集与测试集:将先验数据按一定比例进行拆分。
4. 提取数据特征,将文本解析为词向量 。
5. 训练模型:建立模型,用训练数据训练模型。即根据训练样本集,计算词项出现的概率P(xi|y),后得到各类下词汇出现概率的向量 。
6. 测试模型:用测试数据集评估模型预测的正确率。
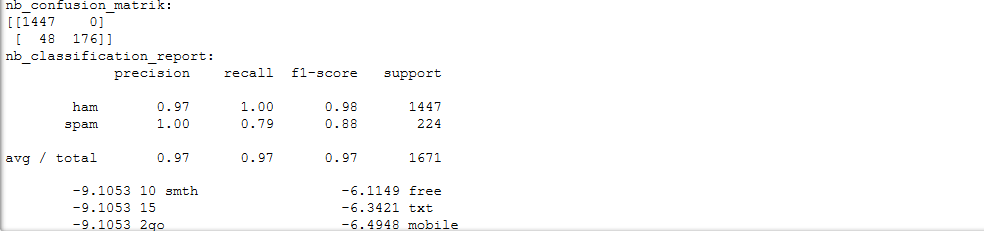
混淆矩阵 ,准确率、精确率、召回率、F值
7. 预测一封新邮件的类别。
#导入nltk数据包import nltkfrom nltk.corpus import stopwordsfrom nltk.stem import WordNetLemmatizer#导入包import csv import numpy as npfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_splitfrom sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrixfrom sklearn.metrics import classification_reporttext = '''As per your request 'Melle Melle (Oru Minnaminunginte Nurungu Vettam)' has been set as your callertune for all Callers. Press *9 to copy your friends Callertune'''#进行邮件预处理def preprocessing(text): text=text.decode("utf-8") # 分词 tokens = [word for sent in nltk.sent_tokenize(text) for word in nltk.word_tokenize(sent)] stops = stopwords.words('english') #停用词 tokens = [token for token in tokens if token not in stops] #去掉停用词 tokens = [token.lower() for token in tokens if len(token) >= 3] #去掉短于3的词 #词性还原 lmtzr = WordNetLemmatizer() tokens = [lmtzr.lemmatize(token) for token in tokens] #将剩下的词重新连接成字符串 preprocessed_text = ' '.join(tokens) return preprocessed_text #读数据file_path = r'C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\ems.txt'ems = open(file_path,'r',encoding='utf-8')ems_data=[] ems_label=[] #保存csv_reader=csv.reader(ems,delimiter='\t') #将数据分别存入数据列表和目标分类列表 for line in csv_reader: ems_label.append(line[0]) ems_data.append(preprocessing(line[1]))ems.close() #将数据分为训练集和测试集,再将其向量化from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_splitx_train,x_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(ems_data,ems_target,test_size=0.3,random_state=0,startify=ems_target)print(len(x_train,len(x_test))) # 将其向量化from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer #建立数据的特征向量vectorizer=TfidfVectorizer(min_df=2,ngram_range=(1,2),stop_words='english',strip_accents='unicode',norm='l2')X_train = vectorizer.fit_transform(x_train)X_test = vectorizer.transform(x_test)import numpy as np #观察向量a = X_train.toarray() for i in range(1000): #输出不为0的列 for j in range(5984): if a[i,j]!=0: print(i,j,a[i,j]) #朴素贝叶斯分类器from sklearn.navie_bayes import MultinomialNBclf = MultinomialNB().fit(X_train,y_train)y_nb_pred = clf.predict(X_test)# 分类结果显示print(y_nb_pred.shape,y_nb_pred) # x-test预测结果print('nb_confusion_matrix:')cm = confusion_matrix(y_test,y_nb_pred) #混淆矩阵print(cm)print('nb_classification_repert:')cr = classification_report(y_test,y_nb_pred) # 主要分类指标的文本报告print(cr) feature_names=vectorizer.get_feature_names() # 出现过的单词列表coefs=clf.coef_ # 先验概率 p(x_ily),6034 feature_log_prebintercept = clf.intercept_ # P(y),class_log_prior : array,shape(n...coefs_with_fns=sorted(zip(coefs[0],feature_names)) #对数概率P(x_i|y)与单词x_i映射n=10top=zip(coefs_with_fns[:n],coefs_with_fns[:-(n+1):-1]) #最大的10个与最小的10个单词for (coef_1,fn_1),(coef_2,fn_2) in top: print('\t%.4f\t%-15s\t\t%.4f\t%-15s' % (coef_1,fn_1,coef_2,fn_2)) #预测一封新邮件的类别。new_email=['新邮件']vectorizer(new_email)clf.predict(new_email)
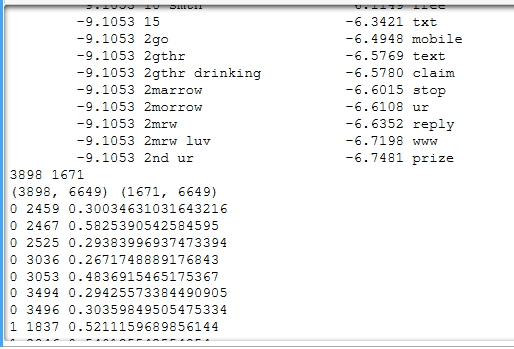
结果: